Explain How Viroids Are Different From Viruses Chegg
If the viral genome is reactivated a productive infection results leading to viral replication and. Microorganisms are beneficial in producing oxygen decomposing organic material.

Solved 32 Viroids Have No Protein And No Capsid Have A Chegg Com
Instead viruses enter living cells and then hijack the hosts cellular equipment to copy viral genetic information build new capsids and assemble everything together.

. One study reported that 25 different viruses were inactivated in 10 minutes with 200 ppm available chlorine 72. Weve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. What is antigenic shift and how might this explain variances different strains of human viruses such as the coronavirus.
Attachment sites are plasma membrane proteins and glycoproteins. This interactive module explores the diversity of viruses based on structure genome type host range transmission mechanism replication cycles and vaccine availability. Describe how prions accumulate in nervous tissue and the appearance of the brain that has been infected with prions.
Animal virus replication 1. Each type has a characteristic cellular composition morphology mean of locomotion and reproduction. Explain how prions and viroids are different.
Viruses only grow and reproduce inside of the host cells they infect. A latent infection develops in the neurons allowing the virus to remain undetected in the host. The replication of a viral genome is a fundamental step in the virus life cycle.
A productive infection results in an explosive viral population cell death and development of disease signs during which neurons are infected. For propagation viruses depend on specialized host cells supplying the. Write one or two sentences describing the role of each structure in the viruss replication process.
Viroids Viroids are infectious entities that affect plants that are smaller compared to a virus. Viroids can be defined as small and naked infectious RNA molecules that cause diseases in higher plants. Viruses are infective agents consisting of a nucleic acid molecule in a protein coat.
Animal virus replication is more complex than phage replication because host cells are more complex. The causative agent of potato spindle tuber disease was discovered by Diener and Raymer. Microbes within the domains Bacteria and Archaea are all prokaryotes their cells lack a nucleus whereas microbes in the domain Eukarya are eukaryotes their cells have a nucleus.
Animal viruses cannot inject their DNA. Virulent phages typically lead to the death of the cell through cell lysis. Start your trial now.
Microorganisms are found in each of the three domains of life. Prions are by far the most dangerous infections caused by the agents already present within the body and are usually fatal. Compare viroids and prions in terms of structure and host.
First week only 499. In experiments using the. There can be few organisms other than humans that have caused such devastation of human animal and plant life.
Viral DNA injected into host cell. Genetic material and protein capsid. The life cycle of bacteriophages has been a good model for understanding how viruses affect the cells they infect since similar processes have been observed for eukaryotic viruses which can cause immediate death of the cell or establish a latent or chronic infection.
The Click Learn incorporates engaging 3D models of 10 different viruses coronavirus rabies influenza A HIV Ebola tobacco mosaic virus TMV. Viruses may be viewed as mobile genetic elements most probably of cellular origin and characterized by a long co-evolution of virus and host. When found outside of these living cells viruses are dormant.
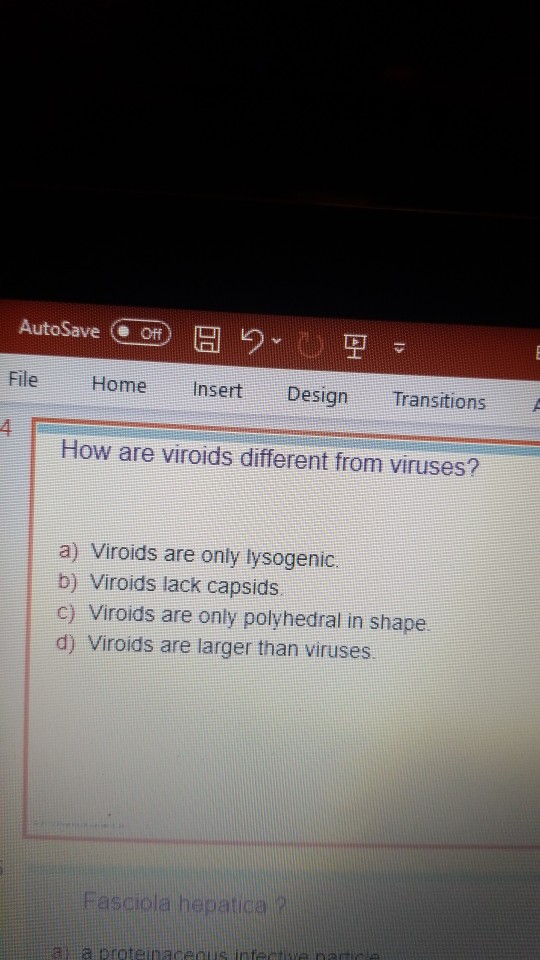
However both types are structurally different from a typical viral particle. Virus A virus is a biological entity that can only reproduce within a host. Explain how prions and viroids are different from viruses.
In this special issue the important role of various viral and host proteins in viral RNA genome. We use the term replicate instead of reproduce to indicate viruses need a host cell to multiply. Bacteria archaea protozoa algae fungi viruses and multicellular animal parasites helminths.
Some microorganisms such as viruses do not fall within any of the. Prions can be defined as small proteinaceous. Tail fibers attach to cell wall proteins.
The viruses contain DNA or RNA as a genetic material but not bothApart from nucleic acid viruses contain protein coat called capsid which is made of subunits called capsomeres. Viruses are made up of protein encapsulating the genetic material whereas viroids are free RNA particles. The main cause of prion diseases is the abnormal folding and clumping of prions in the brain causing brain damage.
For both plus- and minus-strand RNA viruses this process proceeds through a complementary RNA strand intermediate whereas for retroviruses the intermediate is DNA. Viroids cause diseases in plants whereas viruses infect both plants and animals. Solution for Explain how prions and viroids are different from viruses.
Chlorine 500 ppm showed inhibition of Candida after 30 seconds of exposure 54. Explain how the terms COVID-19 SARS-CoV-2 and coronavirus mean different things. Viruses consist of two major parts.
Answers 1 S Sonika. They consist of only nucleic acid without a protein coat. Comparison of Multiplication Cycles of Bacteriophage and Animal Viruses.
Less well known is the huge number of plant viruses that can cause total failure of staple crops. Causes of Prion Diseases. Viruses are not living organisms bacteria are.
A Tobacco Mosaic Virus b Bacteriophage. Several studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of diluted sodium hypochlorite and other disinfectants to inactivate HIV 61. First week only 499.
Lysogeny for phage latency for animal viruses. This leads to memory impairment changes in the personality difficulties in moving. Their life therefore requires the hijacking of the biochemical activities of a living cell.
The diagram below represents a SARS-CoV-2 virus. Viruses are small obligate intracellular parasites which by definition contain either a RNA or DNA genome surrounded by a protective virus-coded protein coat. Microorganisms are divided into seven types.
Start your trial now. Viroids are smaller in size than viruses. Viroids and prions contain either genetic material or protein capsid.
Archaea Bacteria and Eukarya. Save teachers time and engage students with a new simpler interface. Viroids are different from viruses in following aspects.
Smallpox polio rinderpest and foot-and-mouth viruses are all well-known for their disastrous effect on humans and animals. Explain why a virus can only infect specific cells andorganisms. In the table below the diagram identify each of the labeled structures.
Solution for Explain how the attachment of viruses to bacterial cells is different from the attachment of viruses to animal cells.
Solved Fasciola Hepatica A A Proteinaceous Infective Chegg Com
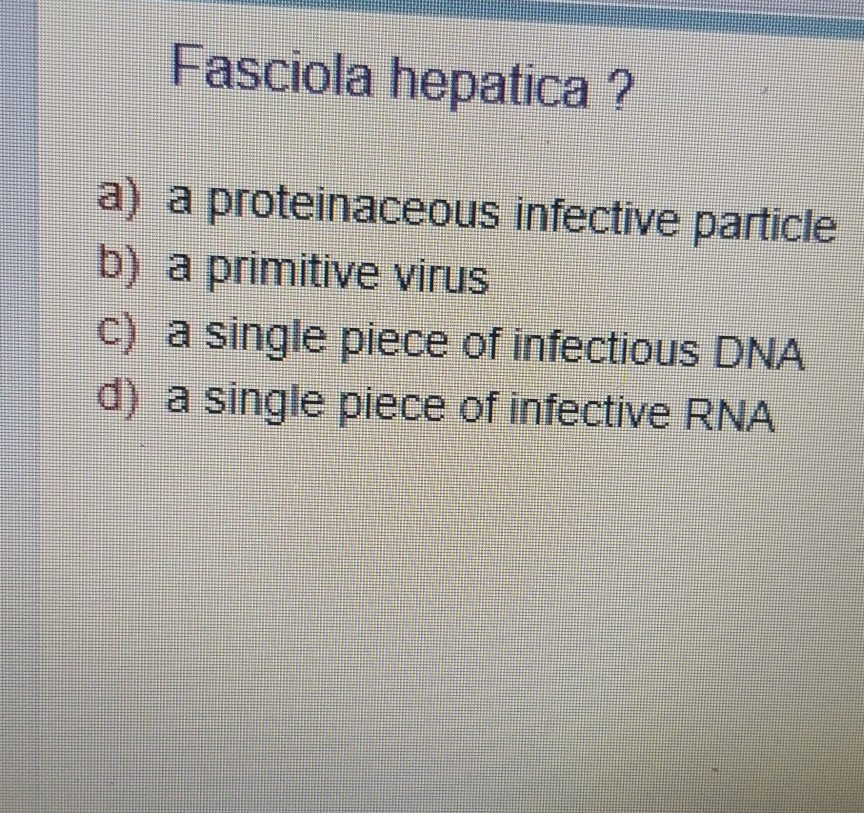
Solved Fasciola Hepatica A A Proteinaceous Infective Chegg Com

Solved Which Of The Following Represents A Difference Chegg Com

Comments
Post a Comment